Dense MgB2 superconducting layer made by diffusion process (IMD)
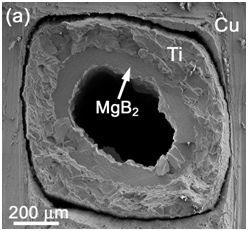
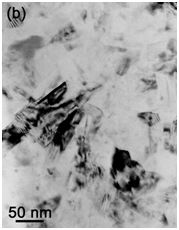 SEM image of IMD MgB2 single wire torn after cooling down by liquid nitrogen (a) and TEM BF image of MgB2layer (b).
SEM image of IMD MgB2 single wire torn after cooling down by liquid nitrogen (a) and TEM BF image of MgB2layer (b).
Microstructure of dense pore-free MgB2 layers in single filament wires made by internal magnesium diffusion process (IMD) have been analysed. The superconducting layer consists of nearly pure MgB2 phase with small volume fraction of nano-sized Mg and MgO precipitates and some of amorphous or nano-crystalline B-rich grains. Content of oxygen in IMD wires was significantly suppressed in comparison to PIT technology. Thin Mg layers were observed on plate-shaped MgB2 grain boundaries. Electrical measurements have shown high critical current densities in MgB2 layer, which are promising for further improvements and also for possible applications.
Rosová, A., Hušek, I., Kováč, P., Dobročka, E., and Melišek, T.: Microstructure of MgB2 superconducting wire prepared by internal magnesium diffusion process, J. Alloys Comp. 619 (2015) 726-732.
Kováč, P., Hušek, I., Rosová, A., Kulich, M., Melišek, T., Kopera, Ľ., and Brunner, B.: Properties of MgB2 wires made by internal magnesium diffusion into different boron powders, Supercond. Sci Technol. 28 (2015) 095014.
Brunner, B., Windbichler, A., Reissner, M., Kováč, P., and Hušek, I.: Comparison of critical current density and pinning behaviour of mono-core MgB2 wires prepared by different method, J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28 (2015) 443-446.





